Restoring AMD-related Vision Loss with SING IMT™
The Smaller-Incision New Generation Implantable Miniature Telescope
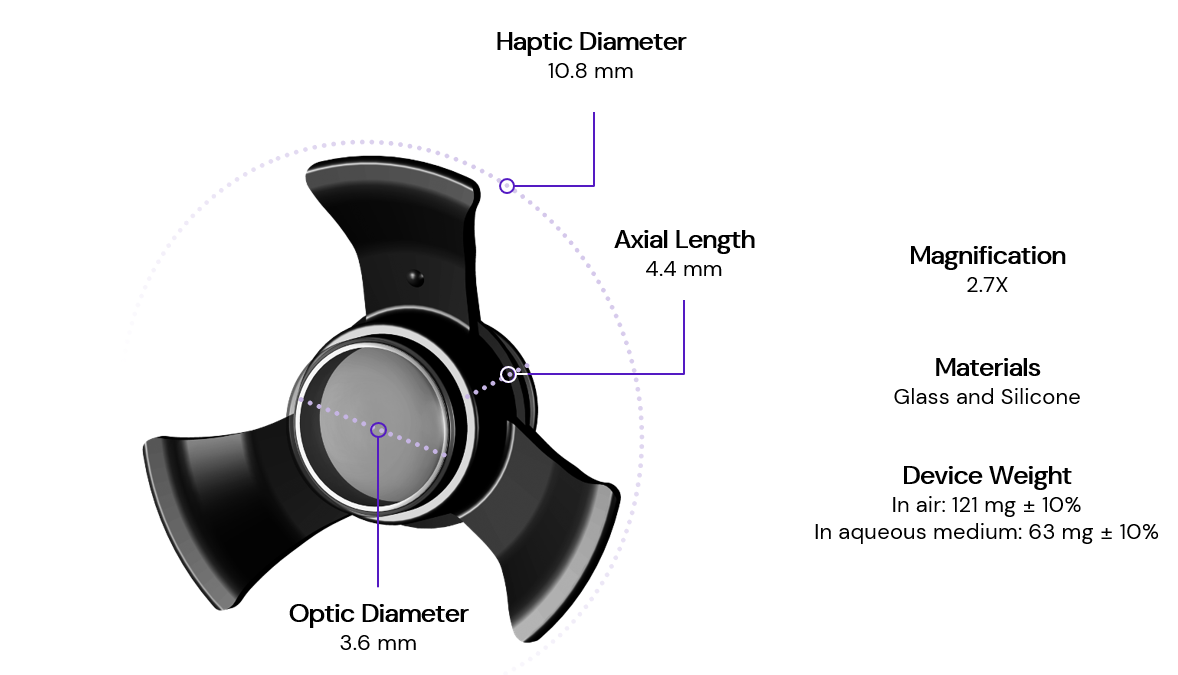
Samsara Vision’s SING IMT is a Galilean telescope implant designed to improve visual acuity and quality of life for patients with late-stage age-related macular degeneration (AMD). The design improves upon a 1st-generation miniature telescope device implanted in more than 600 patients living with late-stage AMD.
SING IMT features the same ultra-precision wide-angle micro-optics optic as its predecessor with an improved haptic design to create a telephoto effect. Images are magnified 2.7x and projected onto healthy photoreceptors surrounding the macula in the back of the eye, reducing the impact of the AMD “blind spot” in central vision and allowing patients to see images that may have been unrecognizable before.